How to Troubleshoot Mazda Car Electrical Issues
How to troubleshoot Mazda car electrical issues – Experiencing electrical problems with your Mazda? From flickering lights to a completely dead battery, electrical issues can be frustrating and potentially dangerous. This comprehensive guide will walk you through troubleshooting common Mazda electrical problems, providing clear, step-by-step instructions and helpful tips to get you back on the road safely and efficiently. We’ll cover everything from simple checks to more advanced diagnostic procedures, ensuring you have the knowledge to address a wide range of electrical malfunctions.
Understanding Mazda Electrical Systems
Before diving into troubleshooting, it’s helpful to understand the basic components of your Mazda’s electrical system. This includes the battery, alternator, starter motor, fuses, relays, wiring harnesses, and various electrical control units (ECUs). Each component plays a crucial role, and a failure in one can trigger problems throughout the system. Understanding their interconnectivity is key to effective troubleshooting.
Key Components and Their Functions:, How to troubleshoot Mazda car electrical issues
- Battery: Provides power to the vehicle when the engine is off.
- Alternator: Charges the battery while the engine is running.
- Starter Motor: Cranks the engine to start it.
- Fuses and Relays: Protect circuits from overloads and control the flow of electricity to various components.
- Wiring Harnesses: Carry electrical signals and power throughout the vehicle.
- ECUs (Electronic Control Units): Manage various vehicle systems, such as engine control, transmission control, and body control.
Common Mazda Electrical Problems and Troubleshooting Steps
Let’s explore some common electrical issues found in Mazda vehicles and how to approach troubleshooting them.
1. Dead Battery
A dead battery is a frequent culprit. First, check the battery terminals for corrosion. Clean them with a wire brush and baking soda solution. Then, use a multimeter to test the battery voltage. A reading below 12.6 volts indicates a weak battery.
If the battery is weak or dead, it might need replacing. However, a consistently dying battery might point to an alternator problem (see below).
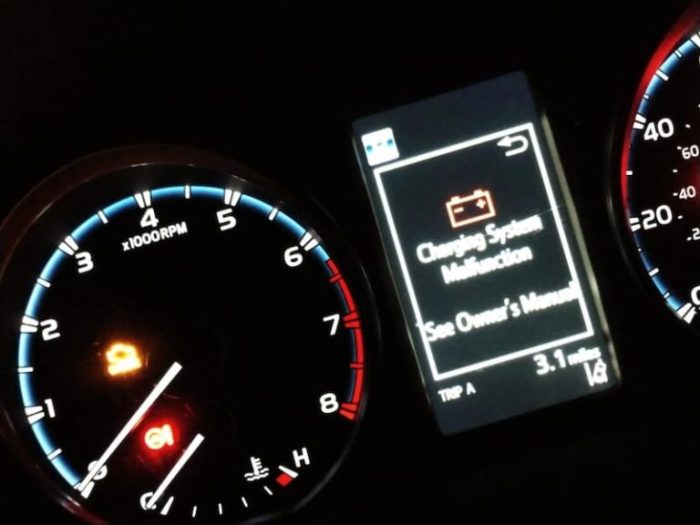
2. Alternator Issues
A faulty alternator prevents the battery from charging. With the engine running, test the battery voltage with a multimeter. It should read around 13.5-14.5 volts. A lower reading suggests a malfunctioning alternator. Professional diagnosis and replacement might be necessary.
3. Starter Motor Problems
If your Mazda cranks slowly or not at all, the starter motor could be the problem. Listen for unusual clicking sounds. A clicking sound often indicates a weak battery or a faulty starter solenoid. A grinding noise suggests issues with the starter motor’s gear meshing. Professional inspection and repair are recommended.
Electrical Component Malfunctions (Lights, Windows, Radio):
Electrical Component Malfunctions (Lights, Windows, Radio):
Problems with individual components like lights, power windows, or the radio often point to blown fuses or faulty relays. Consult your owner’s manual to locate the fuse box and identify the relevant fuse. Replace blown fuses with the correct amperage. If the problem persists, the issue might lie with the component itself or the wiring.
Malfunctioning Electrical Systems (ABS, Airbags, etc.):
Malfunctioning Electrical Systems (ABS, Airbags, etc.):
Issues with advanced systems like ABS brakes, airbags, or electronic stability control require professional attention. These systems are complex and require specialized diagnostic tools. Attempting DIY repairs could be dangerous and void warranties.
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
For more complex electrical issues, you may need more advanced tools and knowledge. These techniques are best left to experienced mechanics.

Source: 2carpros.com
1. Using a Multimeter
Source: autonewsportal.com
A multimeter is an essential tool for diagnosing electrical problems. It can measure voltage, current, and resistance, helping to pinpoint faulty components or wiring issues. Learn how to safely use a multimeter before attempting any electrical testing.
2. Wiring Diagram Consultation
Troubleshooting Mazda electrical issues often begins with checking fuses and the battery. If those are fine, more in-depth diagnostics may be needed, perhaps even consulting a professional. However, before diving into complex repairs, consider the overall reliability of the vehicle; you might find a comparison of similar models helpful, such as this Mazda 3 vs Ford Focus comparison 2025 , to see if electrical problems are a common issue in the Mazda 3.
This research can inform your troubleshooting approach and potentially save you time and money.
Mazda wiring diagrams can be invaluable for tracing circuits and identifying potential problem areas. These diagrams are often available online or through Mazda dealerships.
3. Diagnostic Scan Tools
OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics) scan tools can read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from your Mazda’s ECU. These codes provide clues about potential electrical problems. Many affordable OBD-II scanners are available.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q: My Mazda’s headlights are flickering. What could be the cause?
A: Flickering headlights can indicate a loose connection, a failing headlight switch, or a problem with the alternator or battery. Check connections and fuses first. - Q: My power windows are not working. What should I do?
A: Check the fuse related to the power windows. If the fuse is blown, replace it. If the problem persists, the window motor or its wiring might be faulty. - Q: My car’s dashboard lights are all on. What does this mean?
A: This could indicate a serious electrical problem or a faulty alternator. Have your Mazda inspected by a professional immediately. - Q: How can I prevent electrical problems in my Mazda?
A: Regularly inspect your battery terminals for corrosion, ensure all fuses are in good condition, and have your alternator checked during routine maintenance. - Q: Where can I find a Mazda wiring diagram?
A: You might find them online through forums dedicated to Mazda vehicles, or you can consult your owner’s manual or contact a Mazda dealership.
Resources
- Mazda USA Official Website (for owner’s manuals and contact information)
- AutoZone (for parts and repair information)
- RepairPal (for finding local mechanics)
Call to Action: How To Troubleshoot Mazda Car Electrical Issues
While this guide provides valuable information, tackling complex electrical issues often requires professional expertise. If you’re unsure about any repair, it’s best to consult a qualified Mazda mechanic to avoid further damage or safety hazards. Don’t hesitate to contact your local Mazda dealership or a trusted auto repair shop for assistance.
FAQ Guide
What are the most common causes of Mazda electrical problems?
Common causes include blown fuses, faulty relays, failing alternators, corroded connections, and damaged wiring harnesses. Worn battery terminals are also a frequent culprit.
Do I need special tools to troubleshoot Mazda electrical issues?
A basic multimeter is essential for testing voltage and continuity. A fuse puller and a set of screwdrivers are also helpful. More specialized tools might be needed for more complex repairs.
When should I take my Mazda to a mechanic for electrical repairs?
If you’re uncomfortable working with electricity, or if the problem is complex and beyond your skill level, it’s best to consult a professional mechanic. Also seek professional help if you suspect a short circuit or other potentially dangerous electrical fault.
Can I damage my Mazda’s electrical system by attempting DIY repairs?
Yes, improper repairs can cause further damage. Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on the electrical system. If unsure, consult a professional.





